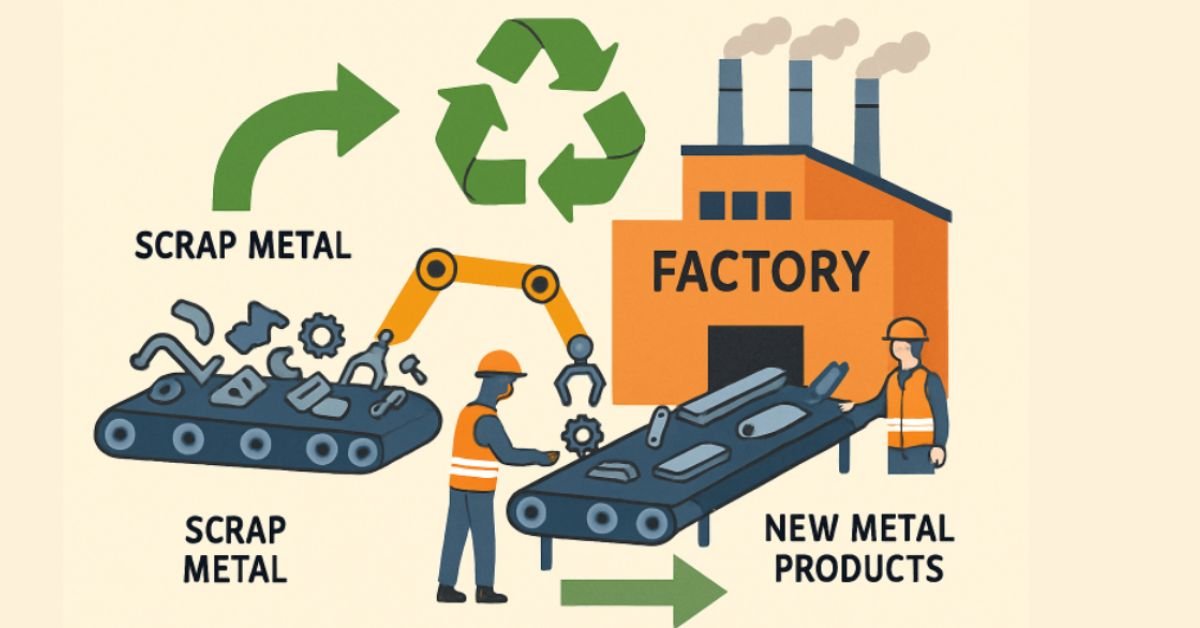
The Environmental and Economic Benefits of Scrap Metal Recycling
Recycling scrap metal is one of the most effective ways to conserve our planet’s finite resources and reduce landfill use. Metals like aluminum, copper, and steel can be recycled infinitely without losing their properties, making them invaluable in efforts to reduce industrial waste and greenhouse gas emissions. For example, recycling aluminum saves up to 95% of the energy required for producing new metal, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This efficiency reduces both environmental footprints and operational expenses for industries, driving the adoption of recycled materials worldwide. Industries are increasingly aware of what can metal be used for after recycling, including construction, transportation, and technology manufacturing.
Financially, using scrap metal reduces the costs associated with mining and refining raw materials. Recycling supports a stable supply of metals, shielding companies from the volatility of global ore markets. As a result, industries that prioritize recycling are better positioned to maintain profitability while advancing environmental stewardship.
Technological Innovations Transforming the Recycling Process
The landscape of scrap metal recycling is evolving rapidly, driven by technological breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and digital tracking systems. AI-powered sensors and robots have vastly improved sorting efficiency, allowing facilities to identify and separate different types of metals with near-perfect accuracy. This precision not only reduces contamination but also ensures that recycled materials meet high-quality standards demanded by manufacturers.
Robotics has automated much of what was once manual labor, resulting in safer workplaces and streamlined operations. These advances are showcased in modern facilities equipped with machine-learning algorithms that adapt and improve over time, setting new benchmarks for the recycling industry. As noted by the BBC, these disruptive technologies are propelling the industry into a new era of efficiency and profitability.
The Role of Recycled Metals in Sustainable Manufacturing
Sustainably manufactured products often rely on recycled metals to limit their environmental impact. The automotive, construction, and electronics sectors are leading examples of industries integrating recycled materials on a large scale. In the automotive industry, for instance, recycled steel and aluminum are used to produce vehicle frames, reducing production emissions and resource consumption.
Electronics manufacturers also depend on recycled precious metals, such as gold, silver, and palladium, to produce circuit boards and connectors, supporting both environmental and economic goals. The use of recycled metals enables companies to meet regulatory requirements, respond to consumer demands for greener products, and improve their overall sustainability metrics.
Global Policies and Market Dynamics Affecting Scrap Metal Recycling
International policy shifts and market dynamics significantly affect how and where scrap metal is recycled. The European Union’s proposed limits on aluminum scrap exports aim to keep valuable materials within domestic markets, ensuring a reliable supply for manufacturers pursuing carbon neutrality. Meanwhile, changes in Chinese import restrictions have reshaped global trade flows, prompting Western countries to invest in better recycling infrastructure rather than exporting their scrap.
These regulatory developments signal the strategic importance of scrap metal in national and global sustainability efforts. They have prompted companies to adopt more transparent supply chain practices and encouraged investment in local recycling solutions. According to Reuters, controlling the flow of recycled metals is now a central element of the transition toward a resilient, sustainable industry.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Scrap Metal Recycling Industry
Like any global enterprise, scrap metal recycling faces numerous challenges. Price volatility for metals, shifting international regulations, and increasing material complexity in manufactured products can all hinder recycling efforts. On the other hand, these obstacles also open the door to innovation. The development of more effective sorting techniques, expanded automation, and digital tracking systems is enhancing the industry’s ability to adapt and grow.
Companies actively investing in research and sustainable practices are better equipped to weather market fluctuations and regulatory uncertainties. Ultimately, the industry’s willingness to innovate will determine its success and continued relevance in the global economy.
Case Study: Recycling Efforts in Post-Disaster Scenarios
Scrap metal recycling also plays a crucial role during crises, especially after natural disasters. In the wake of the Eaton Fire in Altadena, California, for example, emergency crews worked with recycling experts to salvage steel and concrete from damaged properties. Rather than sending debris to the landfill, these materials were processed and reused, helping accelerate environmental recovery and rebuilding efforts. This case demonstrates how scrap metal recycling not only conserves resources but also enhances the resilience and recovery of impacted communities.
Future Outlook: Trends Shaping the Scrap Metal Recycling Industry
Continued investments in AI, robotics, and digital tracking systems will shape the future of scrap metal recycling. As the circular economy concept takes hold, demand for recycled materials is poised to increase across all sectors. New business models focused on take-back and closed-loop recycling systems are emerging, promising longer product lifecycles and reduced waste. Additionally, growing climate awareness and stricter international regulations will press manufacturers and governments to prioritize recycled over virgin materials.
Conclusion
Scrap metal recycling has become a driving force in modern industry, offering a practical solution to environmental and economic challenges alike. Technological innovation, supportive policies, and forward-thinking business strategies continue to advance its role in the transition to sustainable manufacturing. By embracing recycling and investing in new solutions, industries can ensure a cleaner, more resilient future for generations to come.
Ethan Cole is a passionate blogger at Aldalive.com, sharing fresh ideas and engaging content on lifestyle, technology, and everyday trends. With a love for writing and exploring new topics, Ethan aims to make information simple, useful, and inspiring for readers worldwide.