Basic input output system commonly known as BIOS is a firmware interface that initializes and tests your computer’s hardware components before handing control over to your operating system. Think of it as the conductor of an orchestra, ensuring every instrument (your CPU, RAM, storage, and peripherals) is ready to play in harmony.
Why Is BIOS So Important?
Without the BIOS, your PC would be nothing more than a collection of inert parts. It’s the bridge between your hardware and software, making sure everything is in working order before Windows, Linux, or macOS even gets a chance to load.
A Brief History: When Was BIOS Released?
The story of the basic input output system dates back to the dawn of personal computing. But when was BIOS released? The first BIOS was introduced by IBM in 1981, as part of the original IBM PC. This innovation set the standard for how computers would boot and interact with hardware for decades to come.
Fun Fact:
The term “BIOS” was actually coined by Gary Kildall in 1975, but it was IBM’s implementation that brought it into the mainstream.
How Does BIOS Work? A Step-by-Step Look
Let’s break down what happens behind the scenes when you power on your PC:
- Power-On Self Test (POST):
The BIOS checks your hardware—RAM, CPU, graphics card, and more—to ensure everything is functioning. - BIOS Image Loads:
The BIOS image (the actual firmware code) is stored on a chip on your motherboard. This code is executed to initialize hardware. - Boot Device Selection:
BIOS determines which device to boot from—your hard drive, SSD, USB, or even a network. - Hand-off to OS:
Once everything checks out, BIOS hands control to your operating system’s bootloader.
BIOS Image: What Is It and Why Does It Matter?
You might have heard the term BIOS image thrown around, especially if you’ve ever updated your firmware. But what exactly is it?
A BIOS image is simply the compiled firmware code that lives on your motherboard’s ROM chip. It contains all the instructions the BIOS needs to initialize your system. Manufacturers release updated BIOS images to fix bugs, add features, or support new hardware.
Real-Life Example:
“I updated my BIOS image last month to support a new Ryzen CPU. The process was nerve-wracking, but it worked perfectly and my PC runs smoother than ever!”
Where Are BIOS Settings Stored?
A common question is: where are BIOS settings stored? The answer lies in a tiny chip called CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor). This chip retains your BIOS settings—like boot order, system time, and hardware configurations—even when your PC is powered off.
Why CMOS Matters
CMOS is powered by a small battery on your motherboard. If this battery dies, your BIOS settings can reset to default, which is why you might lose your custom configurations after a long period of disuse.
Quick Tip:
If your PC keeps forgetting the time or boot order, it might be time to replace your CMOS battery!
Accessing the PC BIOS is easier than you might think. Usually, you’ll see a prompt like “Press DEL or F2 to enter setup” right after you power on your computer. Once inside, you can tweak everything from boot priority to CPU overclocking.
Common BIOS Settings You Can Adjust
- Boot Order: Choose which device your PC tries to boot from first.
- Hardware Monitoring: Check temperatures, fan speeds, and voltages.
- Security: Set passwords to prevent unauthorized changes.
- Advanced Features: Enable virtualization, tweak RAM timings, or adjust CPU settings.
User Quote:
“I always go into the PC BIOS to set my SSD as the first boot device. It makes startup so much faster!”
Where Are the BIOS Settings Stored? (A Deeper Dive)
You might notice this question comes up a lot: where are the BIOS settings stored? As mentioned, the settings themselves are saved in the CMOS chip, but the BIOS firmware (the code) is stored in non-volatile memory—usually a flash ROM chip soldered onto your motherboard.
What Happens If You Reset BIOS?
Resetting your BIOS (via a jumper or by removing the CMOS battery) will erase your custom settings, but the BIOS firmware itself remains intact. This is a handy troubleshooting step if your PC won’t boot or you’ve made a change that causes issues.
BIOS vs UEFI: What’s the Difference in 2025?
In recent years, many PCs have transitioned from traditional BIOS to UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). UEFI offers a more modern interface, faster boot times, and support for larger hard drives. However, the term “BIOS” is still widely used, even for UEFI systems.
Should You Care?
If you’re building or upgrading a PC in 2025, you’ll likely encounter UEFI. But the core functions—initializing hardware, running POST, and booting your OS—remain the same. Most guides and forums still refer to “BIOS” out of habit.
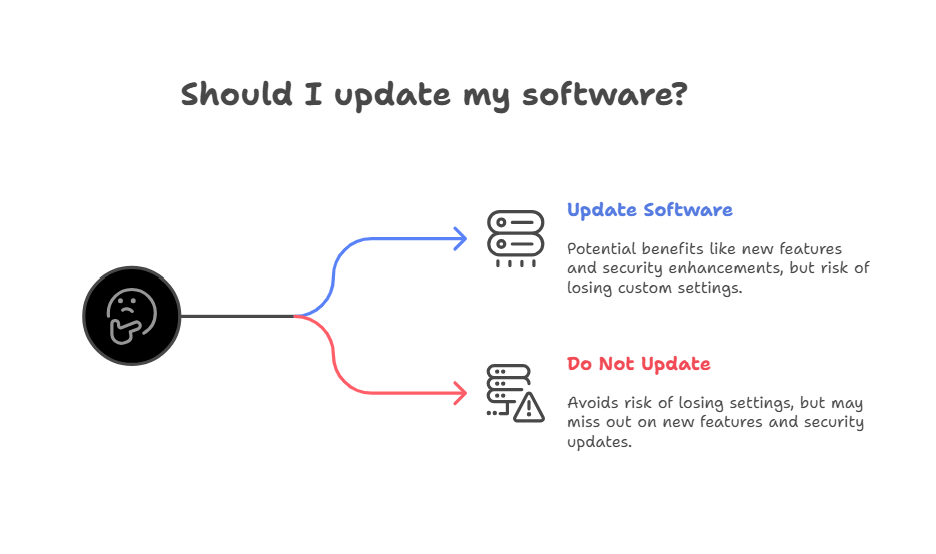
Risks and Rewards: Updating Your BIOS
Updating your basic input output system can unlock new features, fix bugs, and improve compatibility. But it’s not without risks. A failed update can “brick” your motherboard, rendering your PC unbootable.
Pros of Updating BIOS
- Support for new CPUs and RAM
- Improved system stability
- Security patches
Cons of Updating BIOS
- Risk of failed update
- Potential loss of custom settings
- Not always necessary unless you’re experiencing issues
Expert Tip:
Always follow your motherboard manufacturer’s instructions and never interrupt a BIOS update!
BIOS in 2025: Still Relevant or Outdated?
With the rise of UEFI and cloud-based computing, you might wonder if the basic input output system is still relevant. The answer is a resounding yes. Even as technology evolves, the need for a reliable, low-level interface between hardware and software remains.
New Features in Modern BIOS/UEFI
- Graphical interfaces (no more blue screens!)
- Mouse support
- Secure Boot for enhanced security
- Built-in diagnostics and recovery tools
BIOS Image: How to Find and Update Yours
If you’re considering a BIOS update, you’ll need to download the correct BIOS image from your motherboard manufacturer’s website. Always double-check your model number and follow the provided instructions.
Steps to Update Your BIOS Image
- Identify your motherboard model.
- Download the latest BIOS image.
- Copy it to a USB drive.
- Enter BIOS/UEFI and use the built-in update tool.
- Follow on-screen prompts and don’t power off during the update.
Caution:
Never use a BIOS image from a different motherboard model—it can permanently damage your system.
Real-World Uses: Why Tinker with BIOS?
You might be surprised how often enthusiasts and professionals dive into the PC BIOS. Whether it’s overclocking for gaming, enabling virtualization for work, or troubleshooting hardware issues, the BIOS is a powerful tool.
Example Scenario
A gamer wants to squeeze extra performance from their CPU. By adjusting voltage and clock speeds in the BIOS, they can achieve higher frame rates—provided they know what they’re doing!
BIOS Security: Protecting Your System in 2025
As cyber threats evolve, so does the need for BIOS security. Modern BIOS/UEFI systems include features like Secure Boot, which helps prevent malware from loading before your OS.
How to Stay Safe
- Set a BIOS password to prevent unauthorized changes.
- Keep your BIOS updated with the latest security patches.
- Enable Secure Boot if your system supports it.
Troubleshooting BIOS Issues
BIOS problems can be frustrating, but most are fixable. Common issues include failed updates, corrupted settings, or hardware incompatibility.
Quick Fixes
- Reset BIOS to default settings.
- Replace the CMOS battery if settings won’t save.
- Re-flash the BIOS image if it becomes corrupted.
The Future of BIOS: What’s Next?
While UEFI is now the standard, the core principles of the basic input output system remain. Expect even more integration with cloud services, AI-driven diagnostics, and enhanced security features in the coming years.
FAQs
Q. When was BIOS released and who invented it?
A. The first BIOS was released by IBM in 1981 for the original IBM PC, but the concept was introduced by Gary Kildall in 1975.
Q. Where are BIOS settings stored on a PC?
A. BIOS settings are stored in a CMOS chip on your motherboard, which is powered by a small battery to retain information when the PC is off.
Q. What is a BIOS image and why would I need to update it?
A. BIOS image is the firmware file that contains the instructions for your motherboard. Updating it can add support for new hardware, fix bugs, or improve security.
Q. How do I access the PC BIOS on my computer?
A. Typically, you press a key like DEL, F2, or ESC immediately after powering on your PC. The exact key varies by manufacturer.
Conclusion
Basic input output system may not be flashy but it’s the backbone of every PC. Whether you’re a casual user or a tech enthusiast, understanding how BIOS works—and how to manage it—can save you time, money, and headaches.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
John Authers is a seasoned and respected writer whose work reflects the tone, clarity, and emotional intelligence that readers value in 2025. His writing blends deep insight with a natural, human voice—making complex ideas feel relatable and engaging. Every piece he crafts feels thoughtful, original, and genuinely worth reading.

