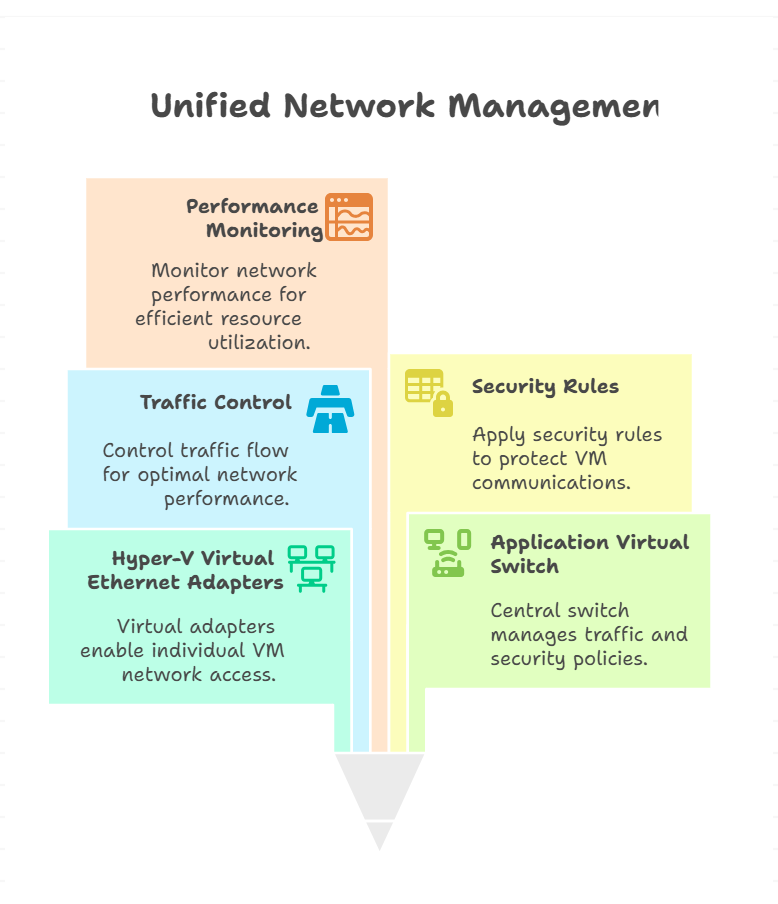
Application virtual switch is a software-based network switch that operates at the application layer, enabling virtual machines (VMs), containers, and cloud-native apps to communicate efficiently within a virtualized environment. Unlike traditional hardware switches, these virtual switches are flexible, scalable, and designed for the dynamic needs of modern IT.
But what does that mean for you? In simple terms, an application virtual switch lets you create, manage, and optimize network connections between virtual resources—without the need for physical hardware. This is a game-changer for businesses running on cloud platforms, using virtualization tools like Hyper-V, or managing complex hybrid networks.
Why Are Application Virtual Switches So Important in 2025?
The digital landscape has changed dramatically. With the rise of remote work, edge computing, and AI-driven applications, network demands are higher than ever. Application virtual switches have become the unsung heroes, quietly powering everything from cloud gaming to enterprise SaaS platforms.
Here’s why they matter:
- Scalability: Instantly add or remove virtual switches as your needs change.
- Security: Isolate traffic, enforce policies, and monitor data flows in real time.
- Cost-Efficiency: No need for expensive hardware upgrades—just configure and go.
- Performance: Optimize traffic routing for low latency and high throughput.
A network engineer recently shared, “Switching to application virtual switches cut our deployment time in half and made troubleshooting a breeze. I can’t imagine going back to physical switches.”
How Does an Application Virtual Switch Work?
Think of an application virtual switch as a digital traffic cop. It directs data packets between virtual machines, containers, and even physical devices, ensuring everything gets where it needs to go—fast and securely.
Key Components
- Virtual Ports: Each VM or container connects to the switch via a virtual port.
- Switch Fabric: The core logic that routes traffic based on rules and policies.
- Management Interface: A dashboard or CLI for configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Real-Life Example
Let’s say you’re running a Hyper-V environment with multiple VMs. You want each VM to access the internet, but also communicate securely with each other. By creating a Hyper-V virtual Ethernet adapter for each VM and connecting them to an application virtual switch, you can control traffic, apply security rules, and monitor performance—all from a single interface.
Setting Up an Application Virtual Switch: Step-by-Step
Ready to get hands-on? Here’s a simplified walkthrough using Hyper-V, one of the most popular virtualization platforms.
1. Open Hyper-V Manager
Launch Hyper-V Manager on your Windows Server or workstation.
2. Access Virtual Switch Manager
Click on “Virtual Switch Manager” in the right-hand pane.
3. Choose Switch Type
You’ll see options like External, Internal, and Private. For most application scenarios, an External switch connects VMs to the physical network, while Internal and Private are used for isolated environments.
4. Create and Configure
Click “Create Virtual Switch.” Assign a name, select the network adapter, and configure settings like VLAN ID, bandwidth limits, and security policies.
5. Attach to VMs
Assign the new virtual switch to your VMs by editing their network settings and selecting the switch.
Tip: If you’re using a Linux environment, you might use commands like 10.2.6 create virtual switches to automate the process.
Application Virtual Switch vs. Traditional Switch: What’s the Difference?
It’s easy to confuse a virtual switch with a physical one, but the differences are huge.
| Feature | Application Virtual Switch | Traditional Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Software-based, instant | Hardware, manual setup |
| Scalability | Unlimited, dynamic | Limited by hardware |
| Cost | Low (no hardware) | High (hardware costs) |
| Management | Centralized, automated | Manual, on-site |
| Security | Granular, policy-driven | Basic VLANs, ACLs |
In 2025, most organizations are moving toward virtual switching systems for their agility and cost savings.
Exploring the Hyper-V Virtual Ethernet Adapter
If you’re working with Microsoft’s Hyper-V, you’ll encounter the Hyper-V virtual Ethernet adapter. This is a virtual network interface that connects your VM to the application virtual switch.
Why use it?
- Flexibility: Easily add or remove adapters as your network grows.
- Isolation: Separate traffic between VMs for security.
- Performance: Optimize bandwidth allocation per VM.
A user recently tweeted, “Hyper-V virtual Ethernet adapter made my lab setup so much easier. No more cable mess—just pure software magic!”
What Is a Virtual Switching System?
A virtual switching system is a broader term that refers to any software-based switching solution, including application virtual switches. It encompasses everything from simple virtual bridges to advanced, policy-driven network fabrics.
Key benefits:
- Centralized Management: Control all your virtual switches from a single dashboard.
- Automation: Use scripts or APIs to create, modify, or delete switches on the fly.
- Integration: Connect with cloud platforms, SDN controllers, and security tools.
How to Create Virtual Switches in Linux (10.2.6 Create Virtual Switches)
Linux admins often use commands like brctl or ip link to create virtual switches. In version 10.2.6 and later, you can automate this process with scripts.
Example:
Bashsudo ip link add name vSwitch0 type bridge
sudo ip link set dev vSwitch0 up
This creates a new virtual switch called vSwitch0 and brings it online. You can then attach virtual network interfaces to this switch, just like in Hyper-V or VMware.
Switch ISO: Deploying Virtual Switches with Prebuilt Images
Some organizations use switch ISO files—prebuilt images that contain all the software needed to deploy a virtual switch. This is especially useful for rapid deployment in cloud or edge environments.
How it works:
- Download the switch ISO from your vendor.
- Mount the ISO in your hypervisor or cloud platform.
- Follow the setup wizard to configure your virtual switch.
This approach saves time and ensures consistency across deployments.
Application Virtual Switch Use Cases in 2025
The possibilities are endless, but here are some of the most common scenarios:
1. Cloud-Native Applications
Modern apps are built to scale across multiple servers and data centers. Application virtual switches enable seamless communication between microservices, containers, and databases.
2. Hybrid Cloud Networking
Connect on-premises resources with public cloud services using virtual switches. This ensures secure, high-performance connectivity without expensive MPLS links.
3. DevOps and Testing Labs
Spin up isolated test environments in minutes. No need for physical hardware—just create virtual switches and connect your VMs.
4. Edge Computing
Deploy virtual switches at the edge to manage IoT devices, process data locally, and reduce latency.
Pros and Cons of Application Virtual Switches
Pros
- Agility: Deploy and reconfigure networks in minutes.
- Cost Savings: No hardware investment required.
- Security: Advanced features like micro-segmentation and policy enforcement.
- Integration: Works with cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments.
Cons
- Complexity: Requires knowledge of virtualization and networking.
- Performance Overhead: Slightly higher CPU usage compared to hardware switches.
- Compatibility: Some legacy systems may not support virtual switches.
Security Considerations in 2025
With great power comes great responsibility. Application virtual switches offer advanced security features, but they also introduce new risks.
Best practices:
- Isolate Sensitive Traffic: Use VLANs and policies to separate critical data.
- Monitor Logs: Regularly review switch logs for unusual activity.
- Update Software: Keep your virtual switch software up to date to patch vulnerabilities.
Real-World Example: E-Commerce Startup
Imagine a fast-growing e-commerce startup. They need to launch new features quickly, handle spikes in traffic, and keep customer data secure. By using application virtual switches, they can:
- Instantly create isolated test environments for new features.
- Scale up during sales events without buying new hardware.
- Enforce strict security policies to protect customer data.
Their CTO says, “Application virtual switches gave us the flexibility to innovate without worrying about network bottlenecks or security gaps.”
FAQs
Q. What is a virtual switching system and how does it work?
A. virtual switching system is a software-based network switch that connects virtual machines, containers, and sometimes physical devices. It works by routing data packets between these resources, enforcing policies, and optimizing traffic flow—all without physical hardware.
Q. How do I create a virtual switch in Hyper-V?
A. Open Hyper-V Manager, go to Virtual Switch Manager, choose the switch type (External, Internal, or Private), and follow the prompts to create and configure your virtual switch. Attach it to your VMs using the network settings
Q. What’s the difference between a Hyper-V virtual Ethernet adapter and a physical adapter?
A. Hyper-V virtual Ethernet adapter is a software-based network interface for VMs, while a physical adapter is hardware installed on your server. Virtual adapters offer more flexibility and can be managed entirely through software
Q. Can I use a switch ISO to deploy virtual switches in the cloud?
A. Yes! Many vendors offer switch ISO files for rapid deployment. Simply mount the ISO in your cloud or virtualization platform and follow the setup instructions.
Final Thoughts
If you’re running modern applications, managing virtual machines, or building cloud-native solutions, an application virtual switch is almost essential in 2025. It offers the agility, security, and scalability that today’s digital businesses demand.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
John Authers is a seasoned and respected writer whose work reflects the tone, clarity, and emotional intelligence that readers value in 2025. His writing blends deep insight with a natural, human voice—making complex ideas feel relatable and engaging. Every piece he crafts feels thoughtful, original, and genuinely worth reading.

