lifetime of tortoise species, compare popular pets like the Russian tortoise, and answer the most common questions about the tortoise life period. If you’re ready to discover the secrets behind these ancient reptiles, let’s get started.
Why Do People Ask: How Long Can Turtles Live?
It’s a question that pops up in pet stores, biology classes, and even on social media. Why? Because turtles and tortoises are often seen as symbols of endurance and wisdom. Their slow movements and calm demeanor make us wonder: What’s their secret to a long life?
One user recently tweeted,
“My grandma’s tortoise is older than my dad. How is that even possible? #turtlepower”
This isn’t just a quirky observation—it’s a real phenomenon. Some turtles and tortoises can live for over a century, making them one of the longest-living animals on Earth. But not all turtles are created equal. Let’s break down the facts.
The Basics: Turtle vs Tortoise Lifespan
Before we get into numbers, it’s important to clear up a common confusion: turtles and tortoises aren’t the same. Turtles generally live in water or spend a lot of time near it, while tortoises are land-dwellers. Their lifespans can differ dramatically.
Average Lifespan of Turtles
- Aquatic turtles (like red-eared sliders): 20–40 years
- Sea turtles (like green sea turtles): 50–100+ years
- Box turtles: 30–50 years, sometimes longer
Average Lifetime of Tortoise
- Pet tortoises (like Russian tortoise): 40–60 years
- Giant tortoises (like Galápagos or Aldabra): 100–150+ years
So, how long can turtles live? The answer depends on the species, environment, and care. Some can outlive your grandchildren!
What Determines a Turtle’s Lifespan?
Let’s get curious for a moment. Why do some turtles live longer than others? Is it just luck, or is there science behind it?
Genetics: The Blueprint for Longevity
Just like humans, turtles inherit genes that influence their lifespan. Some species are simply built to last. For example, the Galápagos tortoise has evolved to survive harsh island conditions, leading to a longer life.
Environment: Home Sweet Home
A turtle’s habitat plays a huge role. Clean water, proper diet, and safe surroundings can add decades to a turtle’s life. Wild turtles face predators, pollution, and habitat loss, which can shorten their lifespan.
Diet: You Are What You Eat
Turtles that eat a balanced diet—rich in leafy greens, vegetables, and the occasional protein—tend to live longer. Overfeeding or poor nutrition can lead to health problems and a shorter tortoise life period.
Care: The Human Factor
Pet turtles and tortoises often live longer than their wild counterparts, thanks to regular meals and protection from predators. But improper care can have the opposite effect.
The Lifetime of Tortoise: Legends of Longevity
When people talk about long-lived animals, the lifetime of tortoise species always comes up. These gentle giants are the Methuselahs of the reptile world.
Famous Old Tortoises
- Jonathan the Seychelles giant tortoise: Born in 1832, Jonathan is still alive and kicking at over 190 years old!
- Harriet the Galápagos tortoise: Lived to 175 years, once owned by Charles Darwin.
These stories aren’t just legends—they’re documented cases. Tortoises have slow metabolisms, tough shells, and a knack for avoiding danger, all of which contribute to their impressive lifespans.
Why Do Tortoises Live So Long?
Scientists believe it’s a mix of slow metabolism, low stress, and evolutionary adaptation. Tortoises don’t rush through life, and that seems to be their secret.
Russian Tortoise Lifespan: A Popular Pet
If you’re considering a pet tortoise, you’ve probably heard of the Russian tortoise. These small, hardy reptiles are favorites among beginners and experienced keepers alike.
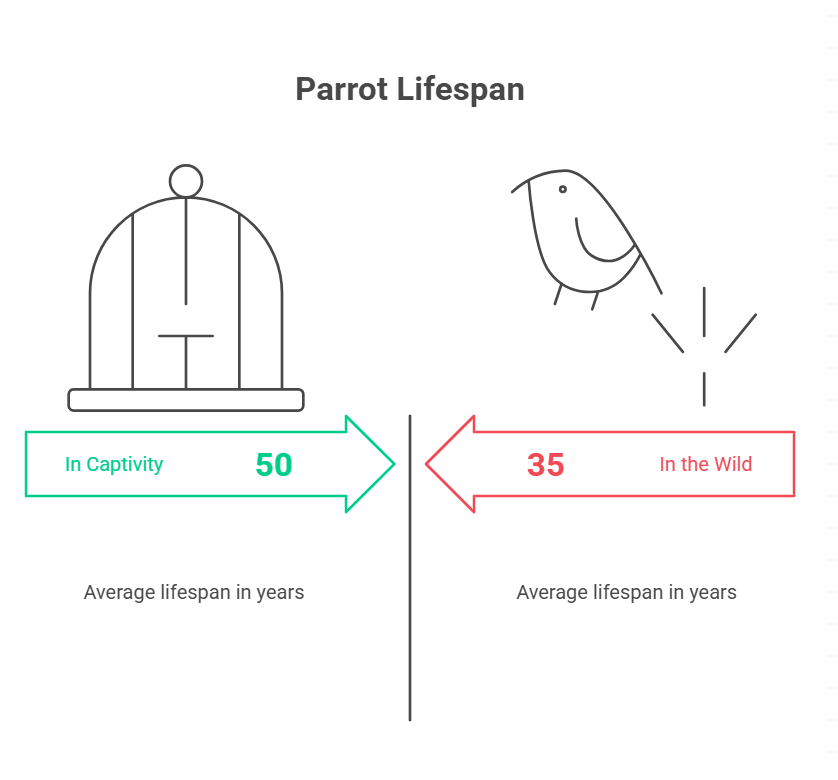
How Long Do Russian Tortoises Live?
- In captivity: 40–60 years, sometimes longer with excellent care
- In the wild: 30–40 years, due to natural threats
The Russian tortoise lifespan is impressive for such a small animal. With proper care, your Russian tortoise could be a lifelong companion—literally!
Real-Life Example
A pet owner shared,
“I got my Russian tortoise in college, and now my kids are taking care of him. He’s part of the family!”
This isn’t unusual. Russian tortoises are known for their resilience and adaptability, making them ideal for long-term pet ownership.
Tortoise Life Period: What to Expect at Each Stage
Understanding the tortoise life period helps you provide the best care at every age. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Hatchling (0–5 years)
- Small, vulnerable, and growing fast
- Needs warmth, humidity, and a safe enclosure
Juvenile (5–20 years)
- More independent, but still developing
- Diet and habitat are crucial for healthy growth
Adult (20–60 years)
- Reaches full size and sexual maturity
- Stable diet and environment needed
Senior (60+ years)
- Slower metabolism, may need special care
- Regular vet checkups recommended
Each stage has its own challenges and joys. Knowing what to expect can help your tortoise thrive for decades.
The Science Behind Turtle Longevity
Let’s get a bit more expert. What does modern science say about why turtles and tortoises live so long?
Slow Metabolism
Turtles and tortoises have incredibly slow metabolisms. This means their bodies use energy at a slower rate, reducing wear and tear on their organs.
Cellular Repair
Some studies suggest that turtles have unique DNA repair mechanisms. Their cells can fix damage more efficiently, which may help prevent age-related diseases.
Low-Stress Lifestyle
Tortoises, in particular, lead low-stress lives. They don’t have many natural predators, and their slow pace means less physical strain.
Evolutionary Adaptation
Over millions of years, turtles and tortoises have evolved to survive in tough environments. Longevity is a survival strategy—living longer means more chances to reproduce.
Risks and Challenges: Why Some Turtles Don’t Live as Long
Not every turtle gets to live out its full potential. Here are some common risks:
Predators and Habitat Loss
Wild turtles face threats from predators, habitat destruction, and pollution. These factors can drastically shorten their lives.
Poor Diet and Care
In captivity, improper diet, lack of UVB lighting, and dirty enclosures can lead to health problems. Shell rot, respiratory infections, and metabolic bone disease are common issues.
Illegal Pet Trade
Many turtles are taken from the wild and sold as pets. This not only harms wild populations but also leads to high mortality rates in captivity.
Pros and Cons of Keeping Long-Lived Turtles as Pets
Thinking about getting a turtle or tortoise? Here’s what you need to know.
Pros
- Long-term companionship: Some turtles can be with you for life.
- Low maintenance: Compared to dogs or cats, turtles require less daily attention.
- Educational: Great for teaching kids about responsibility and biology.
Cons
- Long commitment: You may need to plan for your turtle’s care after you’re gone.
- Specialized care: Proper diet, lighting, and habitat are essential.
- Legal restrictions: Some species are protected or require permits.
Features and Usability: What Makes Turtles Unique in 2025
With advances in pet care and technology, keeping turtles and tortoises has never been easier—or more rewarding.
Smart Enclosures
Modern turtle tanks and tortoise tables come with automated lighting, temperature control, and humidity sensors. These features help mimic natural environments and promote longevity.
Veterinary Care
Exotic pet vets are more accessible than ever. Regular checkups can catch health issues early, extending your pet’s life.
Online Communities
From forums to social media groups, turtle owners can share tips, ask questions, and connect with experts worldwide.
FAQs
Q. How long can turtles live as pets?
A. Pet turtles can live anywhere from 20 to 80 years, depending on the species and quality of care. Some tortoises, like the Russian tortoise, can live 40–60 years or more in captivity.
Q. What is the average lifetime of tortoise species?
A. The average lifetime of tortoise species varies. Smaller tortoises may live 40–60 years, while giant tortoises can surpass 100 years, with some documented cases over 150 years.
Q. How does the Russian tortoise lifespan compare to other pet reptiles?
A. The Russian tortoise lifespan is longer than most pet reptiles. While many lizards and snakes live 10–20 years, Russian tortoises often reach 40–60 years with proper care.
Q. What factors affect the tortoise life period in captivity?
A. Key factors include diet, habitat quality, access to UVB lighting, regular vet care, and stress reduction. Meeting these needs can maximize the tortoise life period and overall health.
Final Thoughts
So, how long can turtles live? The answer is as fascinating as the creatures themselves. From the humble Russian tortoise to the legendary Galápagos giants, turtles and tortoises remind us that slow and steady really does win the race.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
John Authers is a seasoned and respected writer whose work reflects the tone, clarity, and emotional intelligence that readers value in 2025. His writing blends deep insight with a natural, human voice—making complex ideas feel relatable and engaging. Every piece he crafts feels thoughtful, original, and genuinely worth reading.

